Sulfur, with its distinctive yellow hue and pungent odor, has fascinated humans for centuries. But is it a rock or a mineral? In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the world of sulfur, exploring its characteristics, classification, and how it compares to rocks and minerals. Buckle up as we unravel the mysteries of this elemental wonder!
Characteristics of Sulfur
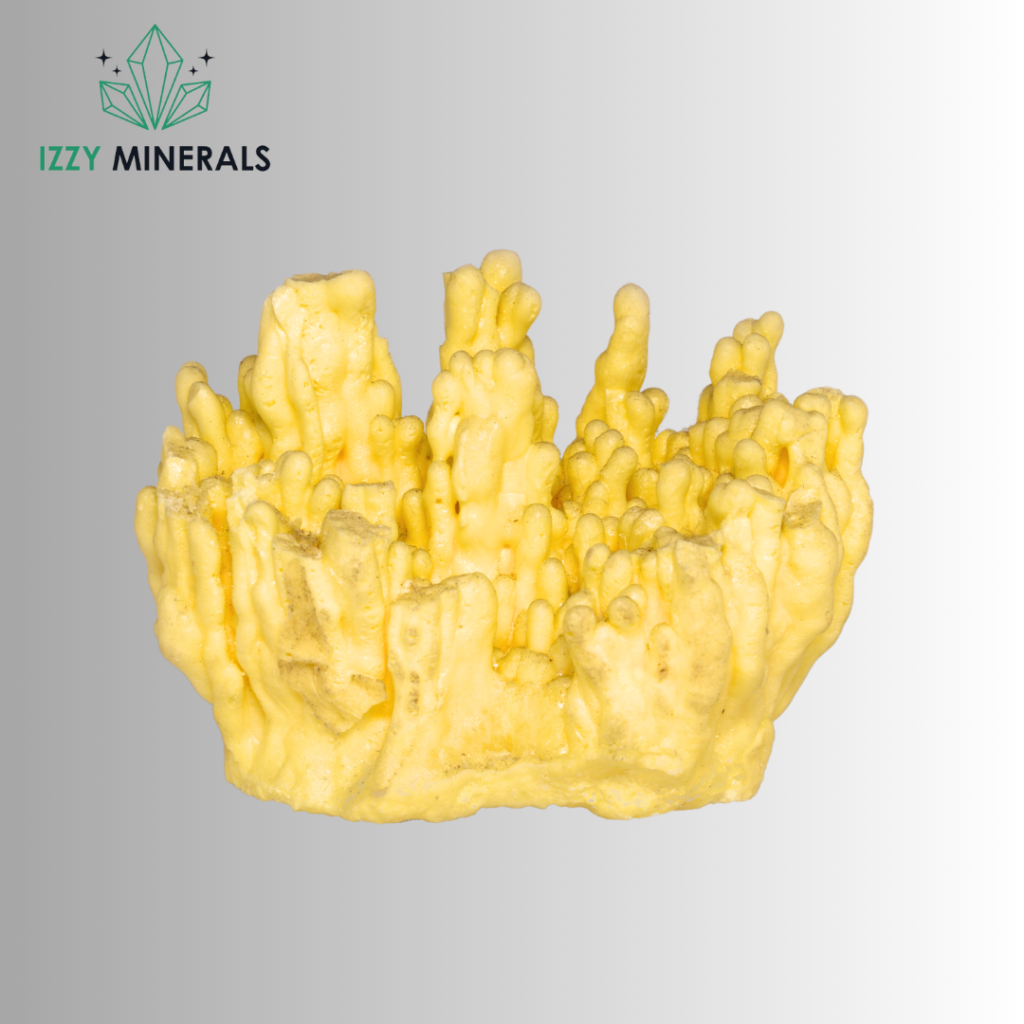
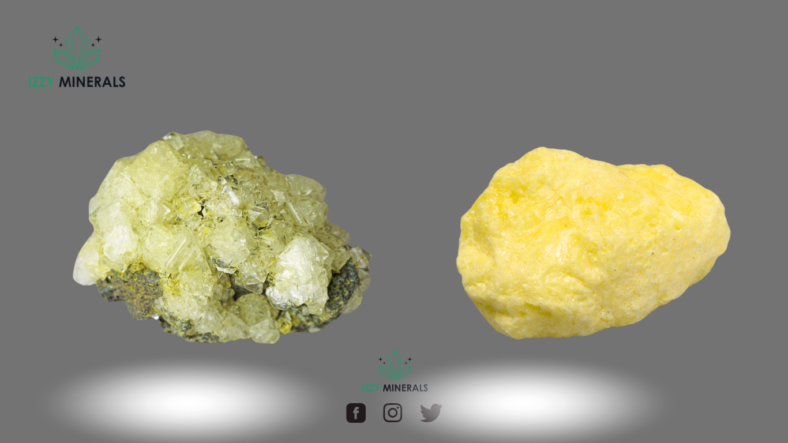
Color: Sulfur appears as a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature.
Versatility: Despite being insoluble in water, sulfur readily forms compounds with almost all elements except a few, such as gold and nitrogen.
Abundance: Sulfur is abundant throughout the Universe, but it’s rarely found in its pure, uncombined form on Earth’s surface.
Chemical Composition: As an element, sulfur is a crucial component of sulfate and sulfide minerals. It also occurs in dissolved ions in various waters.
Classification of Sulfur
Native Element: Sulfur is classified as a native mineral. It forms near volcanic vents and fumaroles, where it sublimates from hot gases. Small amounts of native sulfur also result from the weathering of sulfate and sulfide minerals.
Comparison with Rocks and Minerals
Rocks: Unlike rocks, sulfur isn’t a rock. Rocks consist of various minerals and other materials, whereas sulfur stands alone as an elemental mineral.
Minerals: Sulfur shares some similarities with minerals. It’s crystalline, has diagnostic properties like low hardness and specific gravity, and burns with a blue flame. However, it doesn’t fit the traditional definition of a mineral due to its native state.
Analysis of Sulfur’s Status
Sulfur’s dual existence as both a native mineral and an essential element in compounds makes it unique. Its role in manufacturing sulfuric acid, its use in various products (from insecticides to pharmaceuticals), and its presence in organic molecules within fossil fuels highlight its significance.
FAQs
Is sulfur flammable?
Yes! Sulfur burns with a blue flame, especially when molten.
What causes the smell of rotten eggs?
Sulfur compounds are responsible for the distinctive odor of rotten eggs.
How did the Chinese use sulfur historically?
The Chinese discovered sulfur around 2000 BC and used it to create gunpowder, rockets, and hand grenades.
Conclusion
In the grand geological theater, sulfur takes center stage—a brilliant yellow performer with a fiery secret. So, is sulfur a rock or mineral? It defies easy categorization, dancing between the two realms. Perhaps that’s what makes it truly captivating.

